python使用相关的技巧
1.依赖相关的技巧
1.1 模块路径
(在命令行下,只能识别到当前的路径)
1 | import sys |
1.2 截取字符串s前1024位,不够的位置填充o
1 | '{:o<1024}'.format(s[0:1024]) |
1.3 使用anaconda建立虚拟环境
1 | conda create -n tensorflow pip python=2.7 # or python=3.3 |
1.4 从字符串加载字典
1 | >>> import ast |
1.5 常用的标点符号
1 | puncts = [',', '.', '"', ':', ')', '(', '-', '!', '?', '|', ';', "'", '$', '&', '/', '[', ']', '>', '%', '=', '#', '*', '+', '\\', '•', '~', '@', '£', |
1.5 远程使用服务器的jupyter notebook
1 | jupyter notebook --no-browser --port=8889 |
1.6 配置远程jupyter
搭建远程jupyter notebook,用于代码片段备份,学习碎片日常总结。并在服务器上配置crontab定时任务,推送任务到GitHub。
1.6.1 生成jupyter notebook配置文件
1 | jupyter notebook --generate-config |
记住生成配置文件的目录,一般是在/root/.jupyter 中
1.6.2 生成密文密码
打开ipython3
1 | In [1]: from notebook.auth import passwdIn |
1.6.3 修改配置文件
vim /root/.jupyter/jupyter_notebook_config.py
插入
1 | c.NotebookApp.ip='*' |
1.6.4 启动jupyter
在服务器终端输入: nohup jupyter notebook —allow-root &
1.6.5 实现远程访问
由于本人在开启jupyter时,给的端口是8889,所以需要给阿里云服务器添加安全规则,开放8889端口
终端输入:服务器ip地址:8889
此时,就可以开心的访问服务器端的jupyter
以上参考原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/web_9705/article/details/80421044
1.6.6 配置定时任务
1.6.6.1添加crontab任务
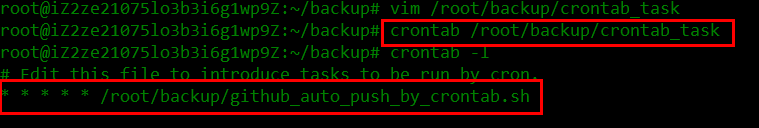
不要使用crontab -e来添加任务,直接用vim编辑好了使用crontab 文件名添加,使用crontab -l验证。
1.6.6.2 编写推送脚本

1.6.6.3 推送结果
1.7 pip 导出依赖包
1 | # 切换环境 |
结果如下:
1 | absl-py==0.6.1 |
2. 代码案例
2.1 使用Python构建HTTP请求,提交数据
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |
1 | # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- |
1 | import requests |
2.2 抓取网页,发送邮件
为了及时获得复试通知的时间,使用python脚本自动间隔访问主页,检索关键字”复试”,当找到关键字后立即邮件通知.这一小段代码包含两个方面的内容,一是网络请求,二是自动发送邮件(我使用的是yahoo的smtp服务器).全部代码如下:
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |
2.3 图像绘制
2.3.1 绘制曲线图
- 代码
1 | import pandas as pd |
- 效果
2.3.2 绘制柱装图
- 代码
1 | import numpy as np |
- 效果
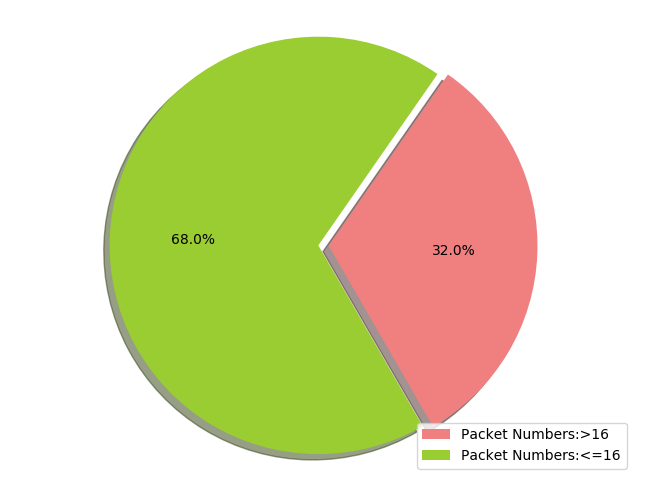
2.3.3 绘制饼装图
- 代码
1 | import ast |
- 效果
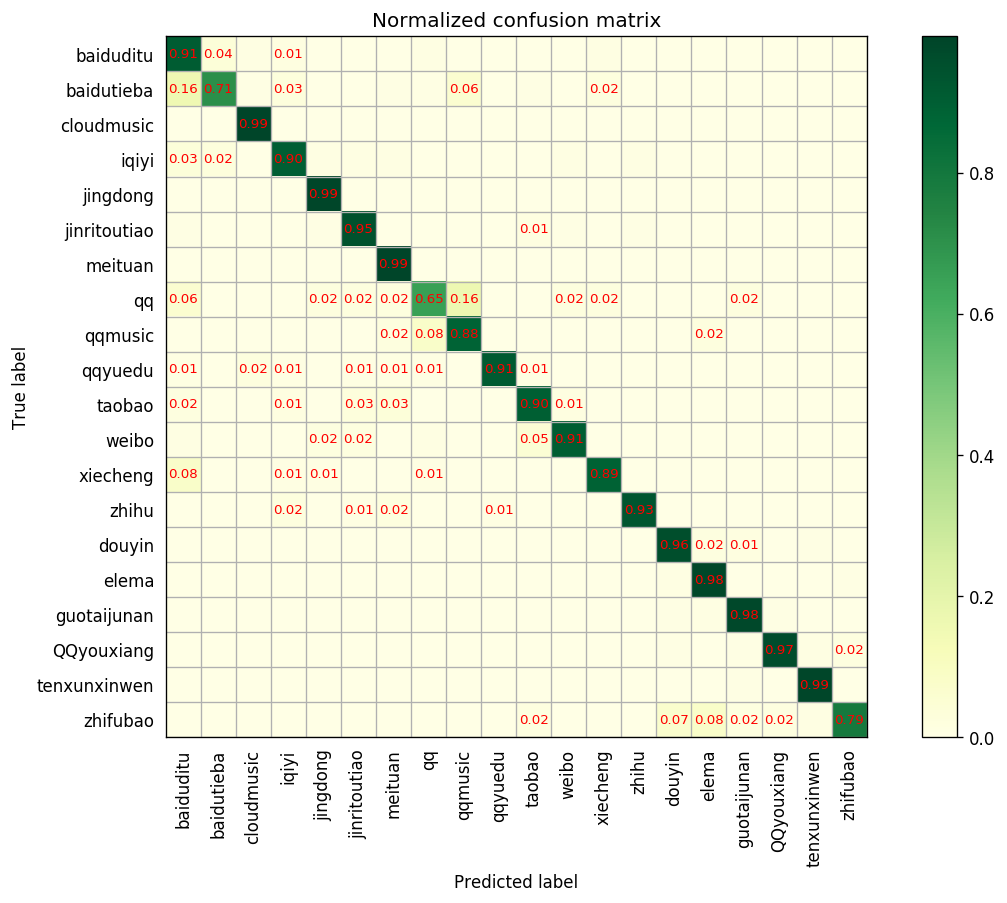
2.3.4 绘制混淆矩阵
- 代码:输入true标签和predict标签自动计算并绘图
1 | #/usr/bin/python env |
- 效果
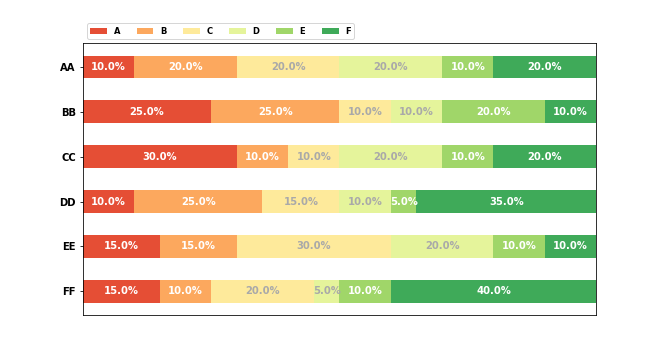
2.3.5 堆积柱状图
1 | import numpy as np |
3. 机器学习深度学习相关技巧
3.1 TensorBoard的使用
3.2 远程连接tensorboard
1 | # 将服务器的端口6006端口重定向到自己的机器上 |
3.3 限制GPU的使用比例
1 | # 针对keras |
3.4 在GPU环境下只加载CPU
1 | # 总有些傻逼的人喜欢占用所有的GPU资源,这时要启动程序得指定仅使用CPU |
3.5 tensorflow log信息可见
1 | tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.INFO) |
3.6 keras自定义Layer
这里以自定义的Attention Layer为例,这个类继承自Layer类,主要需要实现三个函数,一是build,二是call,三是compute_output_shape
1 | class Attention(Layer): |
3.7 TFRecord tutorial
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |
执行结果:
1 | i: 0 |
4. paper相关
4.1 python+Scapy从pcap文件中提取流
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |

