算法基础训练。
实现BitMap
1 | package JavaBasic;/** |
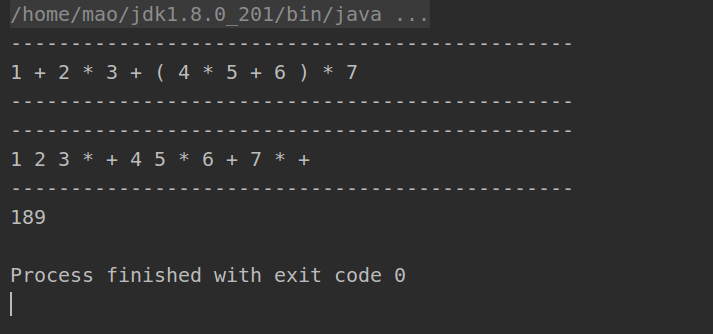
使用中缀表达式实现计算器
1 | package CommonProblems.StackProblems; |
二叉树的遍历
前序遍历
递归
- java实现
1 | public void preorder1(BinaryTreeNode root){ |
循环(使用栈)
- java实现
1 | public void preorder2(BinaryTreeNode root){ |
中序遍历
递归
- java实现
1 | public void inorder1(BinaryTreeNode root){ |
循环(使用栈)
- java实现
1 | public void inorder2(BinaryTreeNode root){ |
后序遍历
递归
- java实现
1 | public void postorder1(BinaryTreeNode root){ |
循环(使用栈)
- java实现
1 | public void postorder2(BinaryTreeNode root){ |
测试
建立二叉树
- java实现
1 | package BinaryTree; |
完整java代码
- 完整
1 | package BinaryTree; |
生产者消费者
要点
- 1 线程 操作 资源类
- 2 判断 干活 通知
- 3 虚假唤醒(必须使用while进行循环)
传统方法:使用synchronized
1 | package JavaDemo.MultiThreadTest; |
使用Lock
1 | package JavaDemo.MultiThreadTest; |
使用阻塞队列
1 | package JavaDemo.MultiThreadTest; |
重写hashCode和equals
What?
- 如果两个对象相等,则hashcode一定也是相同的
- 两个对象相等,对两个对象分别调用equals方法都返回true
- 两个对象有相同的hashcode值,它们也不一定是相等的
- 因此,equals方法被覆盖过,则hashCode方法也必须被覆盖
- hashCode()的默认行为是对堆上的对象产生独特值。如果没有重写hashCode(),则该class的两个对象无论如何都不会相等(即使这两个对象指向相同的数据)
Why?
举两个场景就很明确知道为何要重写了?
- Set中存自定义的对象
- Map中使用自定义对象作为key
以上,如果不重写,即使我们对象的属性值完全相等(就是从意义上完全相等),但是我们new出来的对象是两个不同的对象,那么在加入Set或者作为Map的键时候是会作为unique的,那么添加后,我们会发现意义上一样的值同时存在于Set中,更加不幸的是,我们新建一个对象作为Key去Map中取值会永远也取不到!!!
1 | package JavaBasic; |
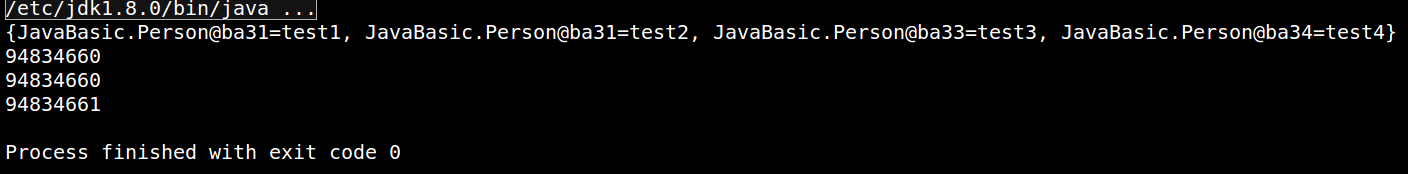
- 重写equals函数和hashCode函数,执行的结果和预期相同
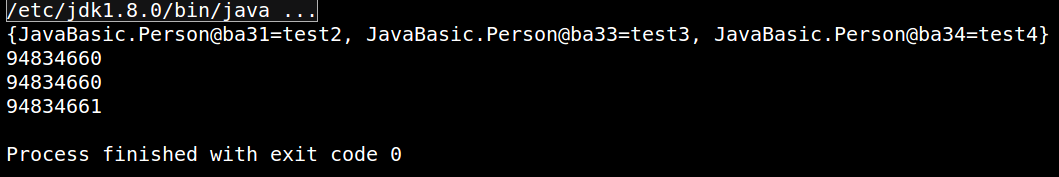
- 只重写了hashCode,发现hashCode虽然可能一样,但是并不能够正确判断对象就是相等的,这也是为什么必须重写equals
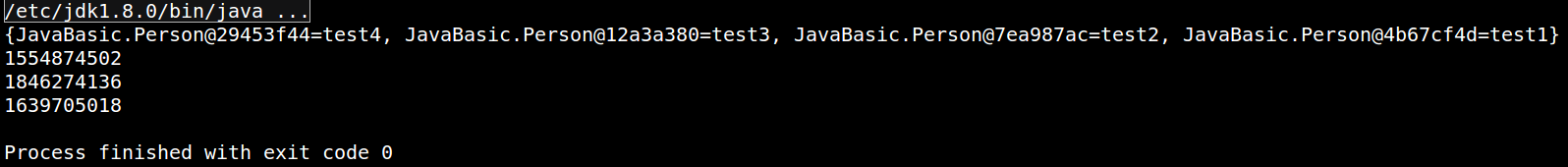
- 均不重写,hashCode不同(当然不能保证完全不同,毕竟有碰撞的存在),对象完全不相等!
How?
重写hashCode:重新计算hash值;重写equals:重写方法:保证对象的每一个属性都有覆盖到,做到完全相等!
- 经典方法
- 借助Objects类
- 借助Apache.commons.lang3
1 | import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.EqualsBuilder; |

